Ideation Techniques: Boost Business Innovation and Creative Thinking
Discover simple ideation techniques to boost creativity and solve business challenges. Explore mind mapping, storyboarding, brainwriting, and more!
October 25, 2024
Coming up with fresh, innovative ideas for your organisation is never an easy task. Too often companies fall into the trap of rehashing the same old strategies in the hope that something will one day stick. So what can your organisation do to avoid lacking innovative ideas when solving challenging business problems and ensure that you always stay one step ahead of your competitors?
One way to breathe new thinking into your projects is by using ideation techniques.
Put simply, ideation is the creative process of generating new ideas, allowing founders and executives to determine the right problems to solve, and how to solve them.
Through ideation, you will be able to: ● Stop oblivious thinking and increase organisational innovation ● Bring diverse perspectives from a wide range of team members ● Uncover unexpected innovative ideas ● Create a higher volume and variety of innovative suggestions ● Drive your team beyond generic thought and ideas
Effective ideation can be achieved through ideation techniques, let’s take a look at some popular ideation techniques that have helped organisations effectively stimulate innovation.
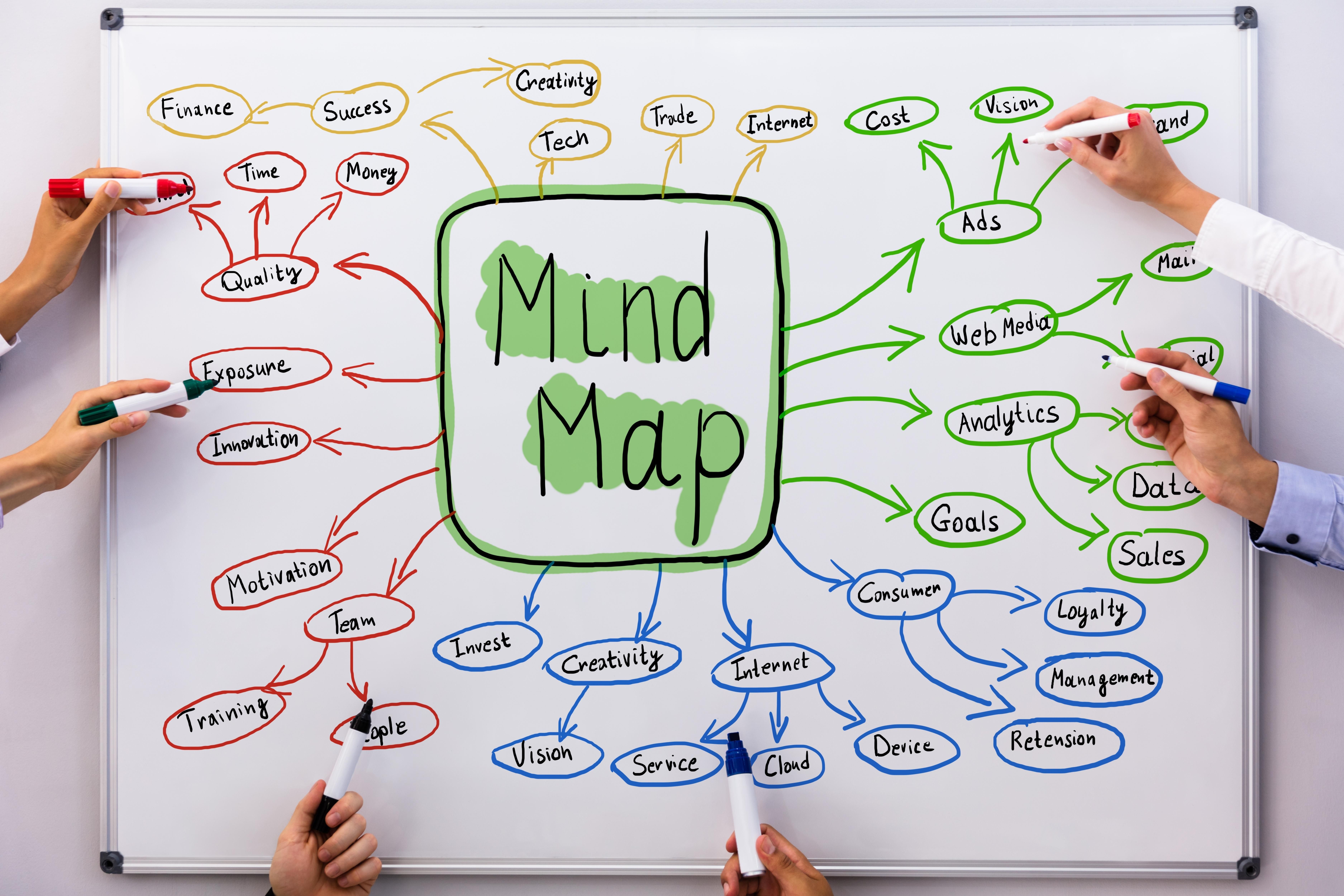
A mind map is an association technique that allows you to organically /organise your thoughts into a non-linear graphic. Concepts, words, images, and thoughts branch out from a central topic, creating a ‘map’ effect that naturally tracks your train of thought.
In the tech world, mind mapping allows developers to create wireframes and site map diagrams without worrying about order or structure, improving overall development efficiency.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐞𝐱𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐭𝐬 𝐬𝐚𝐲…
Graphic organisation techniques have been used for ages, but British psychology author Tony Buzan makes a special case for mind maps.
He claims that traditional brainstorming templates require people to read information in a linear fashion (i.e. from left to right or top to bottom), but the human brain naturally prefers to observe information in a non-linear pattern.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐝𝐨 𝐈 𝐦𝐚𝐤𝐞 𝐨𝐧𝐞?
Here are some basic steps for creating your own digital mind map:
𝐃𝐨𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐥𝐥𝐲 𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐤?
According to a 2017 survey from the Mind Map Software blog, mind mapping can improve your work speed by 44%, increase creativity by 30%, and provide users with 7 hours of extra weekly free time.
Storyboarding involves communicating a story through images displayed in a sequence of panels that maps out a story’s main events chronologically.
Storyboarding involves three main components:
𝟏. 𝐀 𝐬𝐩𝐞𝐜𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜 𝐬𝐜𝐞𝐧𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐨
Based on a user story, a storyboard needs to have a clear description of the scenario you are trying to communicate so that your team can understand what is being depicted prior to looking at the visuals.
𝟐. 𝐕𝐢𝐬𝐮𝐚𝐥𝐬
Each step in the scenario is represented by visuals. These can be lo-fi sketches, illustrations or photos including imagery relevant to the scenario you are trying to depict.
𝟑. 𝐂𝐚𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬
Each visual is accompanied by a caption describing the target user’s actions, environment, device and more. Captions are concise and no more than a couple bullet points
Storyboarding can perform a number of 𝐤𝐞𝐲 𝐟𝐮𝐧𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬 when developing a 𝐔𝐗 𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐠𝐲
𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐔𝐬𝐚𝐛𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐭𝐲
Storyboarding can convey how your users are interacting with your product, summarising this in just text can be useful but images can make the story memorable and easy to skim through.
𝐅𝐢𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐨𝐧 𝐆𝐫𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐝
Visually picturing how your users will interact with your product can make it easier to appreciate their needs and understand which features are needed to prioritise in order to achieve your business goals.
𝐈𝐝𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
Storyboarding can help to visualise your user’s potential experience, allowing you to have a greater understanding of their environment prior to starting the development process. Brainwriting
Brainwriting was designed by German marketing expert Bernd Rohrbach in 1968.
It is a more structured version of a brainstorming technique, with the same goal of generating new ideas, encouraging creative problem-solving, and developing innovative solutions.
The main difference is that instead of discussing the ideas, they are written down. This provides the more shy and introverted participants, who might be reluctant to speak up in brainstorming sessions, an equal opportunity to participate.
𝐀 𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐲 𝐩𝐨𝐩𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐫 𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐞𝐜𝐡𝐧𝐢𝐪𝐮𝐞 𝐢𝐬 𝐤𝐧𝐨𝐰𝐧 𝐚𝐬 𝟔-𝟑-𝟓 𝐛𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐰𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠.
In short, 6 participants, write down 3 ideas on a worksheet within 5 minutes. After the round is done, the worksheets are swapped among participants and another 5 minute round with 3 new ideas is started.
This enables participants to be inspired and build upon other team members’ ideas.
By default, this is repeated 6 times and would generate 108 ideas in 30 minutes.
It’s a pretty straightforward technique, which makes it really easy to implement.
𝐓𝐢𝐩𝐬 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐬𝐮𝐜𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐟𝐮𝐥 𝐛𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐰𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐬𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐨𝐧:
Keep the group size small - no more than 8 participants, as it otherwise becomes difficult to manage.
𝐌𝐨𝐝𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐨𝐫 - having a moderator is not necessary as all the information needed is on the worksheet and the rules are simple.
However, a moderator could still be helpful in making sure that the time boxes are respected.
𝐂𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐥𝐲 𝐝𝐞𝐟𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐝 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦 - same as for brainstorming, all members of the session should be provided with a clearly defined problem statement.
A Morphological Matrix is a form of 𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐨𝐦 𝐬𝐢𝐦𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 that can be used in either a solo or group setting. Its structured table format enables you to expose your ideas to 𝐦𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐢𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐛𝐢𝐧𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬 of business or product possibilities.
This simple tool is best known for bringing a creative element to 𝐰𝐞𝐛𝐬𝐢𝐭𝐞 𝐨𝐫 𝐚𝐩𝐩 𝐝𝐞𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐣𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐬, helping developers to optimise platform 𝐔𝐗 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐔𝐈.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐝𝐨 𝐈 𝐮𝐬𝐞 𝐢𝐭?
Morphological Matrixes can be implemented in four simple steps:
𝐃𝐞𝐟𝐢𝐧𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦. 𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐚𝐫𝐞 𝐲𝐨𝐮 𝐭𝐫𝐲𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐨 𝐜𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐞?
𝐁𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐤 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐭𝐚𝐬𝐤 𝐝𝐨𝐰𝐧 𝐢𝐧𝐭𝐨 𝐭𝐞𝐧 𝐫𝐨𝐰𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐟𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐜𝐨𝐥𝐮𝐦𝐧𝐬, 𝐥𝐚𝐛𝐞𝐥𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐞𝐚𝐜𝐡 𝐜𝐨𝐥𝐮𝐦𝐧 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐚 𝐝𝐢𝐟𝐟𝐞𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐦𝐞𝐭𝐞𝐫/𝐜𝐡𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐢𝐜 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐦. For example, if you are designing a logo, parameters could include font, icon, colour, size, etc.
𝐌𝐚𝐤𝐞 𝐧𝐨𝐭𝐞𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐯𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐮𝐬 𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐞 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐨𝐧𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐬 𝐜𝐨𝐮𝐥𝐝 𝐭𝐚𝐤𝐞, roughly sketching a quick version of each element into the corresponding box.
𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐛𝐢𝐧𝐞 𝐦𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐢𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐞𝐥𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐬 𝐟𝐫𝐨𝐦 𝐞𝐚𝐜𝐡 𝐜𝐨𝐥𝐮𝐦𝐧 𝐭𝐨 𝐬𝐞𝐞 𝐰𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐟𝐢𝐭𝐬 𝐭𝐨𝐠𝐞𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐫 𝐛𝐞𝐬𝐭. These combinations should fuel bigger ideas and help you escape ‘first idea syndrome.’
In American advertising executive Alex Osborn’s words, “𝐈𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐢𝐞𝐫 𝐭𝐨 𝐭𝐨𝐧𝐞 𝐝𝐨𝐰𝐧 𝐚 𝐰𝐢𝐥𝐝 𝐢𝐝𝐞𝐚 𝐭𝐡𝐚𝐧 𝐭𝐨 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐧𝐤 𝐮𝐩 𝐚 𝐧𝐞𝐰 𝐨𝐧𝐞.” That’s why he developed a special method of brainstorming coined 𝐎𝐬𝐛𝐨𝐫𝐧’𝐬 𝐌𝐞𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐝 that uses deferred judgement to overcome a lack of inspiration.
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐢𝐭?
Osborn’s method involves 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐧𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐮𝐩 𝐚𝐬 𝐦𝐚𝐧𝐲 𝐢𝐝𝐞𝐚𝐬 𝐚𝐬 𝐩𝐨𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐛𝐥𝐞, regardless of how outrageous they seem, alongside a ‘𝐩𝐚𝐧𝐞𝐥’ 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐫𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐨𝐟 𝐚 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐝𝐞𝐫, 𝐫𝐞𝐜𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐞𝐫, 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐞𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭 𝐭𝐨 𝐭𝐞𝐧 𝐦𝐞𝐦𝐛𝐞𝐫𝐬. The leader encourages a rapid flow of ideas, the recorder lists every suggested idea, and the panel members supply every idea that comes to them.
𝐖𝐡𝐲 𝐝𝐨𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐭𝐞𝐫?
This method of deferred judgement increases an individual’s 𝐬𝐲𝐧𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐢𝐬 𝐜𝐚𝐩𝐚𝐛𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐞𝐬 by freeing the human mind from traditional analytical thinking patterns and can be useful in the 𝐭𝐫𝐨𝐮𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐬𝐡𝐨𝐨𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐞𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐬𝐨𝐟𝐭𝐰𝐚𝐫𝐞 𝐝𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐥𝐨𝐩𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭.
𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐑𝐮𝐥𝐞𝐬
Three rules are central to Osborn’s method:
𝐈𝐝𝐞𝐚𝐬 𝐬𝐡𝐨𝐮𝐥𝐝 𝐧𝐨𝐭 𝐛𝐞 𝐞𝐯𝐚𝐥𝐮𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝 𝐮𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐥 𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐲𝐨𝐧𝐞 𝐫𝐮𝐧𝐬 𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐨𝐟 𝐢𝐧𝐬𝐩𝐢𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
𝐄𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐲 𝐢𝐝𝐞𝐚 𝐢𝐬 𝐯𝐚𝐥𝐢𝐝
𝐁𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐬𝐡𝐨𝐮𝐥𝐝 𝐨𝐜𝐜𝐮𝐫 𝐢𝐧 𝐚 𝐬𝐚𝐟𝐞 𝐞𝐧𝐯𝐢𝐫𝐨𝐧𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭
To conclude, ideation strategies can be game-changing to eradicate stale and thinking from your ideation.
Thus allowing the people in your organisation to understand the right problems to solve and the right way to approach these problems.
The techniques mentioned in this article should give you a good starting point for how to ideate more effectively, but it is not an exhaustive list, try out different approaches and see which one works best for your organisation!
Bleiben Sie auf dem Laufenden mit allem, was Sie wissen müssen.