
How to Write User Stories: Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
Need help writing user stories? Our guide provides examples, a template, and clear steps to create effective user stories for agile projects.
November 11, 2022
Scrum events are an integral part of the agile framework, serving as key ceremonies within the Scrum sprint. These events provide structure and opportunities for collaboration among team members, ensuring project progress and alignment with goals.
From sprint planning to daily stand-ups and sprint reviews, scrum events keep the team focused and accountable throughout the development process. By participating in these agile ceremonies, teams can identify and address issues early, adapt to changing requirements, and deliver high-quality results efficiently. In this article, we will dive deeper into the various scrum events and their importance in the successful implementation of the Scrum methodology.
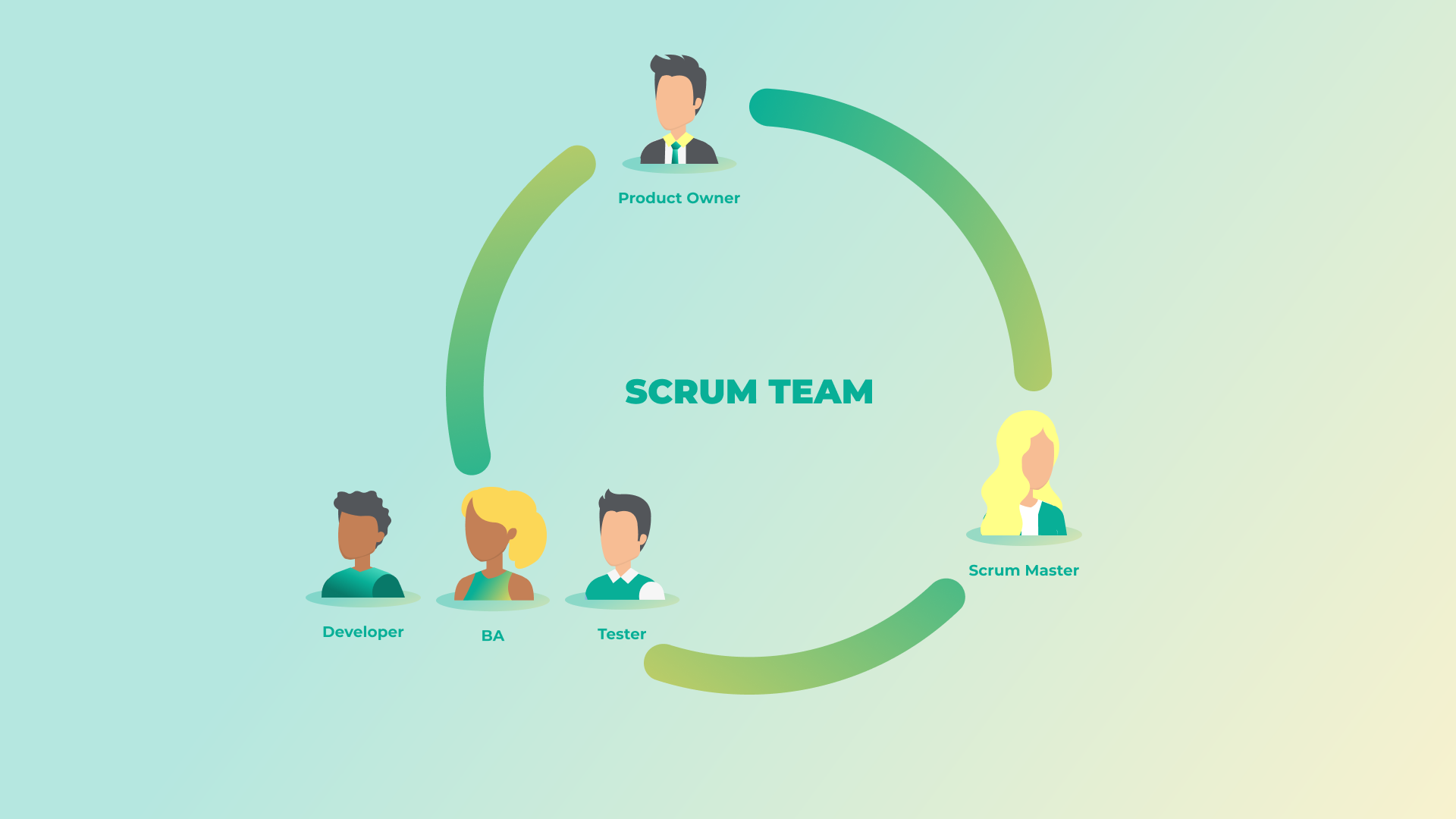
Understanding the five key events in Scrum is essential for decision-makers who oversee development teams and projects. These events ensure that the Scrum team stays aligned, productive, and able to adapt to changes efficiently. Each event serves a specific purpose and helps in achieving the sprint goals and overall project success.
The Sprint Planning event kicks off the start of each sprint. During this event, the Scrum team, including the Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team, collaborates to set the sprint goal and determine the work to be completed. The Product Owner presents the prioritized items from the Product Backlog, and the team discusses and selects items that can be realistically achieved within the sprint's timeframe. The outcome of this meeting is the Sprint Backlog, which includes the tasks and the defined sprint goal. Sprint Planning ensures that the team has a clear direction and plan for the upcoming sprint.
The Daily Scrum, also known as the daily stand-up meeting, is a brief meeting that takes place every day of the sprint. It usually lasts a maximum of 15 minutes and is attended by the entire Scrum team. The purpose of the Daily Scrum is to inspect the progress towards the sprint goal and adapt the Sprint Backlog as necessary. Each team member shares what they accomplished the previous day, what they plan to do today, and any obstacles they are facing. This event promotes transparency, fosters communication, and helps the team stay focused and coordinated.
The Sprint Review is held at the end of each sprint. During this event, the Scrum team presents the Increment, which is the potentially shippable product increment developed during the sprint, to the stakeholders. The team demonstrates the new features and functionalities, and the stakeholders provide feedback. This collaborative session allows the Scrum team to inspect the work done and adapt the Product Backlog based on the feedback received. The Sprint Review ensures that the product is continually improved and aligned with customer needs and expectations.
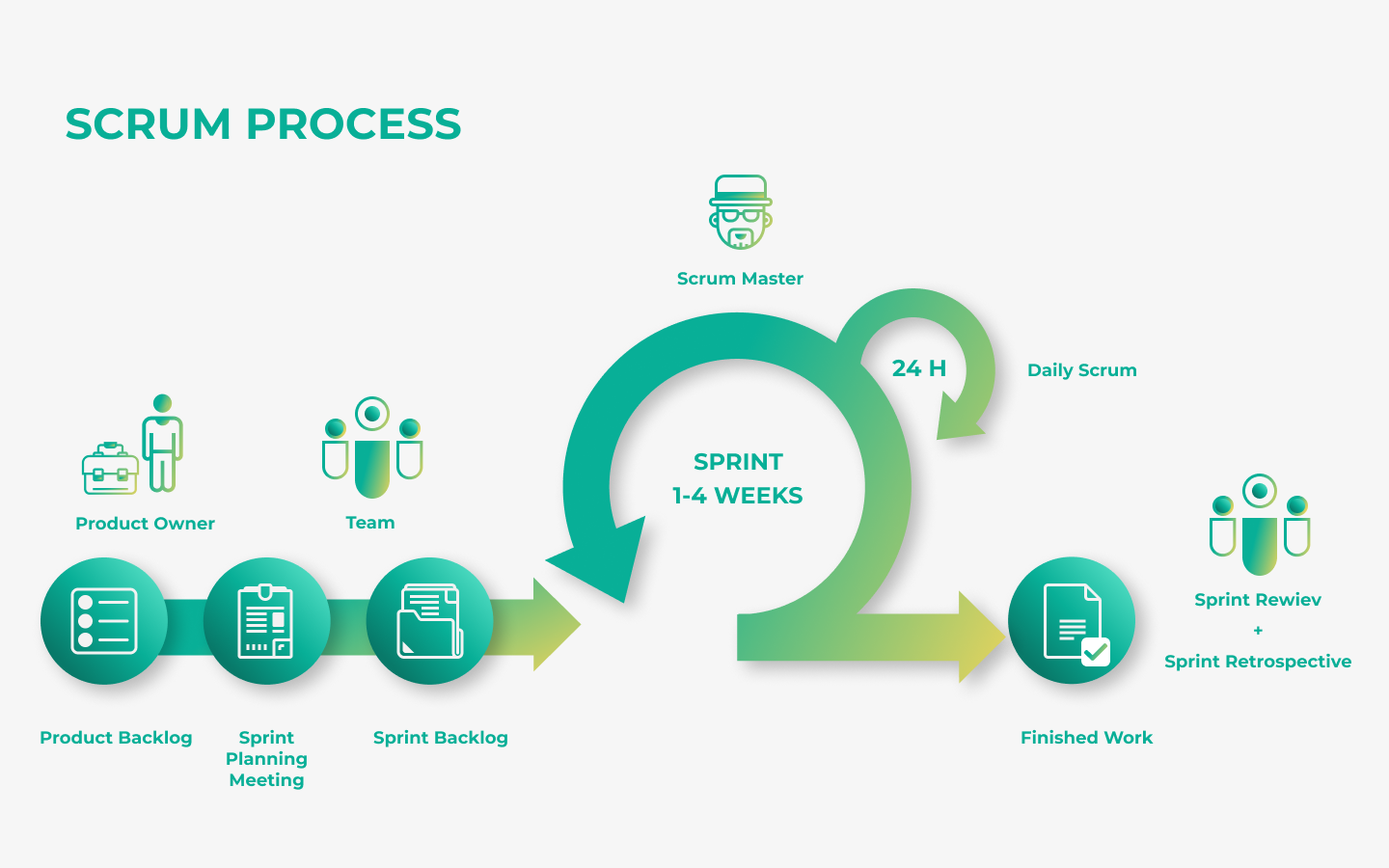
The Sprint Retrospective is the final Scrum event of the sprint and takes place after the Sprint Review. The goal of the Sprint Retrospective is for the Scrum team to reflect on the sprint process and identify areas for improvement. The team discusses what went well, what didn’t, and what could be improved in future sprints. This event fosters a culture of continuous improvement by allowing the team to make necessary adjustments to enhance their performance and processes. The insights gained from the retrospective help in making the next sprint more effective.
Backlog Refinement, also known as backlog grooming, is an ongoing activity that involves the Scrum team reviewing and updating the Product Backlog. The Product Owner, along with the Scrum team, discusses the backlog items, clarifies requirements, and re-prioritises tasks as needed. This event ensures that the Product Backlog remains current and that items are ready for future sprints. Regular refinement sessions help the team to better understand the upcoming work and prepare for Sprint Planning meetings more effectively.
Mastering the five key Scrum events—Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective, and Backlog Refinement—is essential for decision-makers overseeing development teams and projects. These events ensure clear communication, continuous improvement, and effective adaptation to changes, ultimately enhancing project success and organisational efficiency. By thoroughly understanding and implementing these Scrum events, teams can achieve their sprint goals more efficiently and deliver high-quality products that meet stakeholder expectations.
Bleiben Sie auf dem Laufenden mit allem, was Sie wissen müssen.

Need help writing user stories? Our guide provides examples, a template, and clear steps to create effective user stories for agile projects.

Learn how to calculate and interpret sprint velocity in Scrum. Find out common challenges and best practices to enhance your team's performance.

Understand the essential goals of sprint planning: objectives, team collaboration, backlog prioritization, and more. A guide for executives.